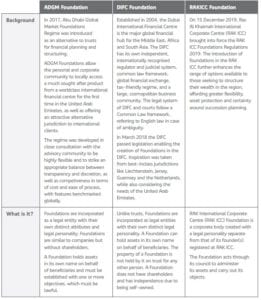
Despite the current global uncertainty which the world has, and continues to face with COVID-19, the UAE is continuing to develop its suite of financial planning and structuring tools to compete with other global markets.
Following the implementation of the ADGM and the DIFC Foundations, we saw the RAKICC Foundation introduced in December 2019. These three unique solutions have provided much needed flexibility for asset protection and succession planning and are proof of the focus and determination that the jurisdiction wants to become a leading powerhouse in financial services.

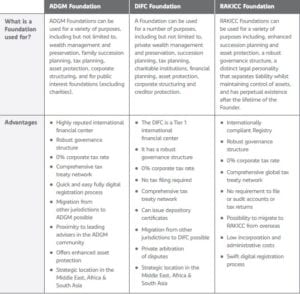
What’s a Foundation?
A Foundation is an incorporated vehicle into which assets can be placed, set-up on the instructions of an individual or company, with separate legal personality. But, unlike a company, it doesn’t have shareholders. The Foundation owns the title to such assets however, it’s administered on behalf of beneficiaries who can enjoy the benefits of the assets.
Foundations – a flexible approach for clients who wish to have a greater degree of control and influence over the administration of their assets.
Foundation characteristics
- A Foundation is created under the law of the specific state
- Has a judicial (corporate personality)
- Can have no beneficial ‘owner’
- Holds title to assets in its own right
- Perpetual or limited existence
- Assets donated, transferred, borrowed or acquired
- Structure depends on jurisdiction legislation
- Usually cannot have commercially orientated aims
- Beneficiaries rights enshrined in regulations / by-laws
UAE Foundations
Case study
- A UAE holding company that owns and operates a shopping mall and some other retail and leisure establishments in the UAE. The operational businesses and physical assets are directly owned by the family’s patriarch.
- The client wishes to consolidate his businesses and assets under one structure that will offer asset protection while maintaining a level of control. He also wishes to have Shariah-compliant succession planning in place for his family.
- The client had previously consolidated all operational entities under a single holding company structure. This along with his physical assets will be placed into the Foundation as the final piece of the Corporate structuring.
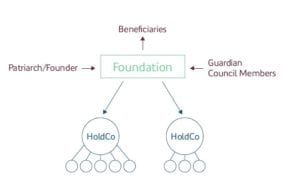
- The Foundation now holds the assets in its own name on behalf of beneficiaries. All assets are now segregated from individual direct ownership through the Foundation. The patriarch who is the founder can amend, revoke or vary the terms of the charter, by-laws or objects of the Foundation or terminate the Foundation during his lifetime.
- Council Members and a Guardian are appointed to ensure the Foundation operates as it was intended to do, with the Council Members adhering to the by-laws and the Guardian overseeing the Council members’ duties.
- Finally, the Foundation gives the family privacy as information relating to beneficial ownership of private Foundation is not placed on a public register and is not accessible to the public. This information is kept by the governing Authority and only released at their discretion for legitimate purposes.
A legal entity
Through a Foundation, the founder can transfer assets to the new legal entity which becomes part of the Foundation’s structure rather than their personal wealth. The Foundation creates a council which will manage the assets in accordance with its rules. These can be for the support of the beneficiaries of a cause, purpose or charity. A Foundation’s concept is derived from civil law jurisdictions, as opposed to a trust which is a common law concept.
If you’d like to discuss any of the above with us, please get in touch.